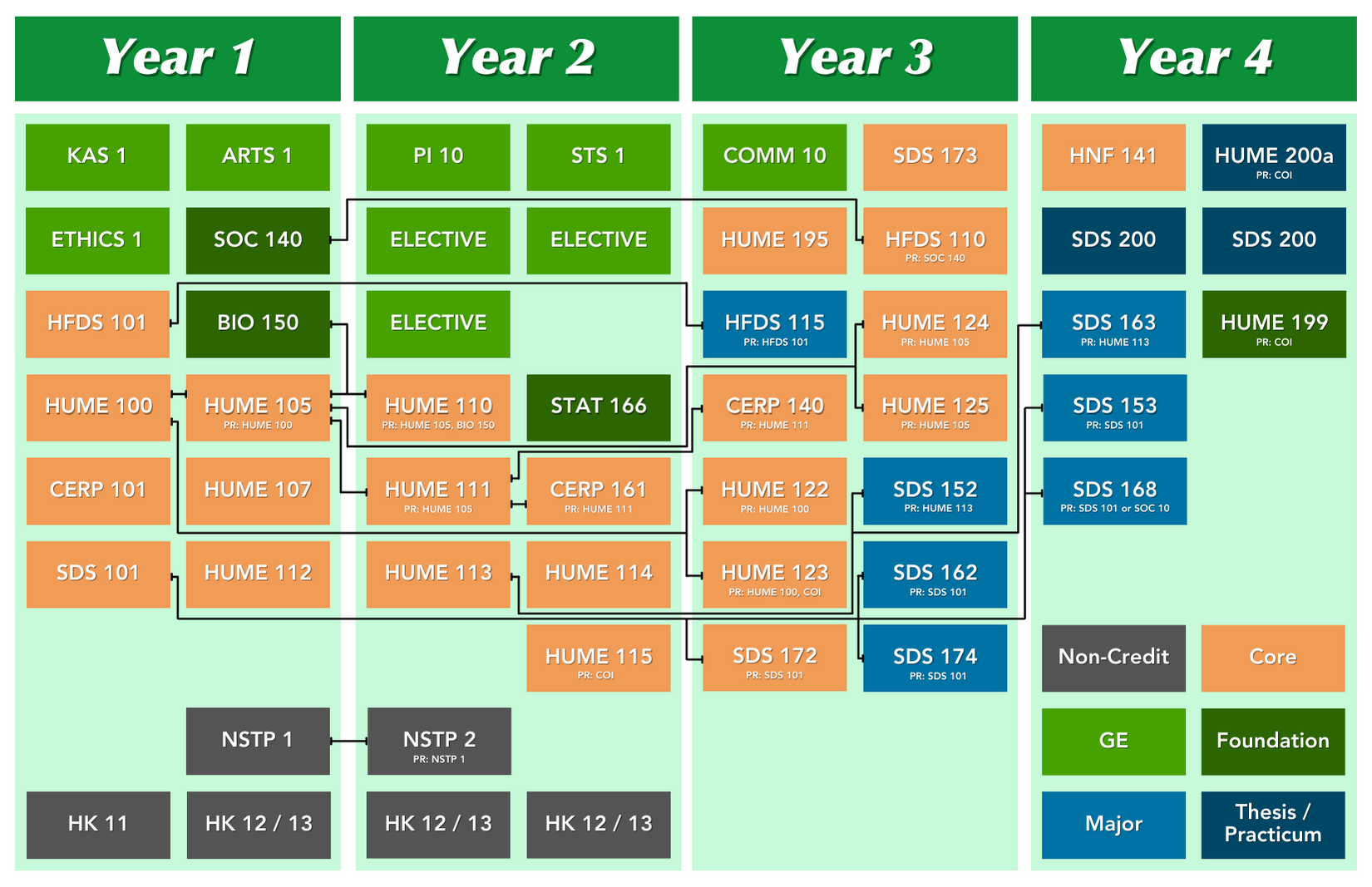
COURSES OFFERED
2018 BS HUMAN ECOLOGY MAJOR IN SOCIAL TECHNOLOGY
PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES
- Articulate and discuss the latest developments in their specific field of practice and engage in life-long learning;
- Effectively communicate orally and in writing both English and Filipino Languages;
- Work effectively and independently in multidisciplinary and multi-cultural teams;
- Demonstrate professional, social and ethical responsibility, especially in practicing intellectual property rights and sustainable development;
- Preserve and promote “Filipino historical and cultural heritage”;
- Apply social science concepts and theories to the analysis of social and ecological issues;
- Design and execute research using appropriate approaches and methods;
- Articulate principles, theories and methods of human ecology in an organized, culturally sensitive and credible manner;
- Engage in authentic learning opportunities through continuing education research and collaboration with local and international institutions;
- Practice ethical values in decision making in relation to human ecological issues, interventions and in everyday life;
- Apply holistic, responsive and relevant solutions to local, national and global human ecological issues;
- Evaluate complex and environmental problems and concerns using a human ecological; and
- Lead with honor and excellence in public service and in fields of practice.
Course Listing
◼ HUME 100
◼ HUME 112
◼ HUME 113
◼ HUME 115
◼ HUME 123
◼ HUME 199
◼ HUME 200a
◼ SDS 101
◼ SDS 152
◼ SDS 153
◼ SDS 162
◼ SDS 163
◼ SDS 168
◼ SDS 172
◼ SDS 173
◼ SDS 174
◼ SDS 200
◼ HUME 100
Introduction to Human Ecology
Core Course For Freshmen Other Courses
Course Description: The course aims to introduce the history of human ecology including nature, scope, ideologies, perspectives of the discipline and its application.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- explain the nature and scope of human ecology;
- trace the development of human ecology as a perspective and academic field of study;
- articulate human ecology as a non-traditional discipline; and
- discuss areas of concerns and possible fields of application in Human Ecology.
◼ HUME 112
Sustainability Science
Core Course For Freshmen Social Development and Social Development Values
Course Description: The course provides a hands-on, experiential learning experience as it provides opportunities for the discourse of concepts and emerging perspectives, and introduces the student to the tools and techniques in sustainability studies including practices that work which will enable students to employ critical and creative thinking in addressing complex and dynamic socio-environmental concerns in society today.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- discuss the basic concepts in, and history of sustainability science and its current development directions;
- explain the human-environment interaction affecting sustainability;
- examine principles, models and integrative research methods used to assess sustainability; and
- analyze applications of sustainability principles.
◼ HUME 113
Community Study and Human Welfare
Core Course For Sophomores Social Services and Development Values
Course Description: Analysis of communities as to social and physical structure, functions, resources technology and levels of living; implications on community and human welfare.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- explain the community theories;
- describe the community as a social system;
- discuss the setting factors of a community;
- articulate the operations of the communities as a system; and
- analyze the relationships and interactions of the major community systems and its component parts.
◼ HUME 115
Social Policies
Core Course For Sophomores Social Development and Social Development Values
Course Description: A look into social and resource policies-based analysis of problems and approaches as well as introduction to benefits and costs in human, social, economic, political and environmental terms.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: COI
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes:
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- recall the benefits and costs of specific social policies;
- explain the concepts of social policies;
- develop research / case study showcasing examples of effective or ineffective social policies;
- determine the operational and institutional requirement for social policy implementation;
- apply the process which will lead to sound social policy making; and
- assess social policies that will ensure the harmonious relationship between human and its environment.
◼ HUME 123
Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction in Human Ecosystems
Core Course For Juniors Social Services and Development Values
Course Description: Concepts, frameworks, models, tools and methodologies of climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction and their applications to human ecosystems.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: HUME 100, COI
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- explain the key concepts in disaster, hazard, vulnerability and disaster risk reduction;
- discuss vulnerability and capacities;
- articulate the legal bases of disaster risk reduction and management in the Philippines;
- articulate the principles, process and significance of Community- Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (CBDRRM);
- distinguish the roles of key players and social institutions in DRRM in the Philippines;
- analyze the interaction among hazards, vulnerability and disaster risk in the Philippines in relation to biophysical, socioeconomic, and political conditions;
- determine the appropriate Participatory Hazard Assessment tools that can be employed in the community for risk reduction and disaster management; and
- design research / case study showcasing the relationship of sustainable livelihood framework in reducing vulnerability and in promoting effective delivery services in development.
◼ HUME 199
Seminar in Human Ecology
Foundation Course For Seniors Other Courses
Course Description: Review and discussion of current issues in Human Ecology and related fields.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: COI
Units: 3.0
◼ HUME 200a
Supervised Field Experience
Thesis / Practicum For Seniors Other Courses
Course Description: Social Technology majors are to participate in on-going community-based social development programs of development agencies and other institutions. Specifically, their involvement is in developing/strengthening the capabilities of human interest group and organizations toward a more effective and sustainable management of human-environment interaction. In the process, the students gain insights into developmental problems, needs, capabilities and potentials of human and institutional organizations in interacting with the habitat-environment.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2, M
Pre-requisites: COI
Units: 6.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- test and integratively apply the transdisciplinary knowledge, attitude and skills in leadership, human resource development, organizing, mobilizing and management of social organizations/institutions for more effective and sustainable management of human-environment interaction;
- demonstrate sensitivity to the aspirations of people and their organized strength in improving their social conditions; and
- apply capabilities in leadership, human resource development, organizing and mobilizing and management to ensure effective social organizations.
◼ SDS 101
Introduction to Social Development
Core Course For Freshmen Social Development and Social Development Values
Course Description: History, perspectives, trends, approaches, and contemporary issues and problems of social development.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- identify the growth of social development as an area of concern;
- discuss the various perspectives of social development;
- demonstrate the different approaches of social development;
- compare social development trends within human ecological framework;
- analyze issues and problems in planning and implementing social development programs; and
- evaluate the role of technology in social development.
◼ SDS 152
Community Services and Programs
Major Course For Juniors Social Services and Development Values
Course Description: Services and programs designed to assist the development of the community; analysis of approaches and techniques for bringing about development.
Semesters Offered: 2
Pre-requisites: HUME 113
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- explain the concepts, theories and principles in planning, organizing, implementing and evaluating community programs and services;
- discuss the different community programs and services;
- interpret some approaches in the delivery of community services;
- differentiate the processes in the delivery of community services and programs;
- examine the interrelationship of the different community services and programs;
- differentiate the processes in the delivery of community services and programs; and
- articulate the importance of community services and programs for human welfare.
◼ SDS 153
Adult Programs in Social Development
Major Course For Seniors Social Services and Development Values
Course Description: Organization and management of adult programs towards social development with emphasis on extension work, teaching methods and experiences for successful adult learning and in working with adults.
Semesters Offered: 1
Pre-requisites: SDS 101
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- identify concepts about adults;
- explain the relevance of adult programs in social development;
- analyze the organization and management of social development programs for adults;
- apply concepts about adults;
- develop social development programs for Adults; and
- design extension and teaching methods appropriate in adult learning and in working with adults.
◼ SDS 162
Design and Management of Training Programs
Major Course For Juniors Organizational and Institutional Development
Course Description: Concepts and principles, formulation , evaluation and implementation of training programs.
Semesters Offered: 2
Pre-requisites: SDS 101
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- express the importance of training in social development;
- explain the theories, principles, and conditions toward an effective training program;
- compare the effectivity of proposed programs to existing training programs;
- organize a training program in relation to social development; and
- evaluate training programs in social development.
◼ SDS 163
Social Vulnerabilities and Capacities
Major Course For Seniors Organizational and Institutional Development
Course Description: Principles and methods in the assessment of the vulnerabilities and capacities of social-ecological systems in the content of a changing environment.
Semesters Offered: 1
Pre-requisites: HUME 113
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- discuss the key concepts and principles in the study of vulnerabilities and capacities of human ecosystems;
- explain the various frameworks and approaches in social vulnerability and capacity assessment;
- apply the methods and procedures of social vulnerabilities and capacities assessment in the conduct and analysis of cases;
- analyze the vulnerabilities and capacities of selected human ecosystems; and
- critique selected approaches to vulnerability and capacities assessment.
◼ SDS 168
Social Impact Assessment
Major Course For Seniors Organizational and Institutional Development
Course Description: Principles and methods in the assessment of the social impacts of planned interventions on human ecological systems.
Semesters Offered: 1
Pre-requisites: SDS 101 or SOC 10
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- discuss the historical, philosophical and theoretical bases of the social impact assessment (SIA);
- explain the role and scope of SIA in relation to the environmental impact assessment (IEA) process;
- discuss the various applications of SIA;
- apply the principles and methods in analyzing, monitoring, and managing social impacts;
- conduct research / case study showcasing the SIA process;
- analyze the types of social impacts that can result from critical development proposals and projects; and
- evaluate planned interventions in terms of their impacts on human ecological systems.
◼ SDS 172
Techniques in Community Organizing
Core Course For Juniors Organizational and Institutional Development
Course Description: Techniques and practice in organizing human-centered development groups.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: SDS 101
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- identify the appropriate concepts, elements, philosophy and principles of community organizing in the field;
- explain the concepts, theories, elements, philosophy and principles of community organizing;
- analyze different community based organizations in the Philippines in terms of the models and approaches used;
- explain the characteristics, skills and values of a community organizer;
- explain and apply the different CO processes in the country and in the world;
- design different organizational development approaches / models relevant to the Philippine setting; and
- evaluate the community-based program/project for development being implemented in a particular community organization.
◼ SDS 173
Consumer Education
Core Course For Juniors Organizational and Institutional Development
Course Description: Problem, issues and challenges on safety, labeling and advertising of goods and services as these relate to the consumer in the market; the effects of social and economic policies on consumer behavior and human welfare.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- define consumer and consumer education;
- Discuss the role of consumer education in protecting consumers and promoting societal well-being;
- analyze the interrelatedness of needs, motivations and behaviors of consumers;
- propose a consumer research affecting consumer behaviours and public policies;
- apply the skills learned in consumer education; and
- evaluate the consumer research that affected consumer behaviours and public policies.
◼ SDS 174
Filipino Values and Social Development
Major Course For Juniors Social Development and Social Development Values
Course Description: Nature and concepts of values; approaches to values development; application of Filipino values in the management of social development programs.
Semesters Offered: 2
Pre-requisites: SDS 101
Units: 3.0
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the course, students should be able to:
- discuss the various concepts/nature of values;
- identify the strengths and weaknesses of selected Filipino values;
- compare the direct and indirect approaches to values development; and
- analyze the application of Filipino values in the management of ecologically-oriented social development programs.
◼ SDS 200
Undergraduate Thesis
Thesis / Practicum For Seniors Other Courses
Course Description: Conduct of theses on Social Technology and Human Ecology.
Semesters Offered: 1, 2
Pre-requisites: None
Units: 6.0